Nothing has been as extensively discussed as the problem of medical care in the US. Discussions have caused for many years outrage between two poles: between the exponents of the HMOs and of the private health insurance and those who side with a system where public control is more effective.
While debating the healthcare issue, can we be concentrating on things that might be incorrect? Instead of contemplating whether the public is better than private or vice versa, it would be much beneficial for us to consider the developments in the business world. Learning the good sides of that world and adapting it into the medical system, we can achieve a less expensive and more fruitful system.

Chapter 1 – Disruptive technology can render healthcare less expensive and available to more people
The issue of healthcare is one of the issues of the utmost importance which the US confronts. In order to access healthcare, one has to spend money like water. Amelioration is largely possible.
Two courses of action are available before us: One is running the healthcare system as if it is a business; the other is employing disruptive technology in the healthcare system to make it more available and affordable. You may have learned disruptive technology now for the first time. However, many money-making industries in diverse fields of business, such as automotive and financial ones, already employ disruptive technology.
Then, what does disruptive technology signify?
Also known as disruptive innovation, disruptive technology consists of three components:
A technological enabler is the first one. This novelty renders it easier to find solutions to issues through making solutions into a matter of routine, which helps the whole operation become more inexpensive. Business model innovation is the second one. It gives firms the chance of providing their services cheaper and making their services more available while they still profit.

An example is IBM, which was utilizing disruptive technology when it took on a new business model which moved its company’s operations to Florida, far away from where their business operations took place, namely New York and Minnesota
By selecting this action, they did not have to deal with the overhead costs, unit volumes, or to pay the high-margins, with all of which they had to tackle when they were in the north of the country.
This not alone explains how they achieved success. Through a technological enabler, they underpinned their business innovation: the microprocessor. The blend of an innovative, cheaper business strategy and their exceptional invention resulted in their radically transforming the computer market after having launched the first computer for individual use.
The IBM case gives a lucid account of one beneficial aspect of using disruptive technology, which is the fact that it makes things cheaper and at the same time renders products and services more available.
What is the last component, then?
The third one is a value network, which is basically a foundation consisting of numerous firms, each of which is innovative and has reciprocally-strengthening business models. Consider a firm producing microprocessors. For a value network to be formed, each firm partaking in the process, from those who supply to those who transport, should take on disruptive technology and each firm would profit.
Now that you have learned what disruptive technology means, we can move on to the separate kinds of disruptive business models.
Chapter 2 – In utilizing the capacity of disruptive technology, it is vital to have an ingenious business model.
As many business people are aware, conducting research on the market is important and they will expend large amounts of money to understand the consumers’ preferences. They do this since it guides them toward which products to focus themselves on. However, in spite of the fact that this is a prevalent method, it is very injudicious.
What is the reason for this?
The answer is that there is a more advantageous way toward a profiting business model that is adapted to consumer wants: disruptive technology carried out by means of a business model, the operation of inventively reconsidering the business model to secure it gives your consumers what they wish for.
How to do it?
For a business model to be genuinely innovative and bring success, markets should be defined in terms of jobs rather than products, which means that you should adjust yourself to the consumers’ wants to understand what they want from a product rather than launching a product and then finding your consumers.
By embracing this strategy, one of the fast-food companies in the US achieved great success. Upon reconsidering their business operation, they figured out that more than 40% of their milkshake product was purchased by bored commuters during the mornings. They figured out that they had not much time and wanted to get a quick snack to appease their stomach growling.

Knowing this, the company changed its milkshakes to bigger and thus enduring ones, in compliance with their consumers’ wants, to satisfy their consumers by occupying them while they are on their way to work.
Briefly, through an innovatory rethinking of their market, they ameliorated their product (and greatly increased their gainings) by adapting to the wants of their consumers.
What is also crucial is to encase your product in such a way that it serves the want of your consumers. For instance, by promoting their product as virtually a meal by its very nature, the fast-food company created such a good strategy that they sold a lot of milkshakes.
Chapter 3 – Healthcare could be radically transformed by the help of the aforementioned business innovation models.
Alright, you know now the way the model of business innovation functions; however, how would it reform healthcare?
Through separating the of general hospitals and general physicians into three different models of business:
The first model is solution shops, which are businesses detecting and remedying unorganized problems and are at the same time charging consumers on the basis of fee-for-service. Some of the businesses adopting this strategy are consultancy firms, advertising agencies, R&D firms.
The second is Value-Added-Process businesses that make precious products out of unfinished ones. Their way of billing is based on a fee-for-outcome system. Car producers, retailers, and CVC’ MinuteClinic, which defines prices in accordance with the procedure it has, are part of this model.

The last model is facilitated networks. These companies either bill their customers for memberships or by the transaction. The best examples of this model are eBay-like firms, mutual insurance companies, the model of curing persistent sicknesses utilized by dLife, a networking company for families and patients of diabetes.
What makes splitting the traditional system into three business models a fine idea? It is because the most pioneering shifts occur when a business model takes the place of another, despite the fact that such shifts can come about in a business model itself.
Fortunately, a simple three-step process can help you realize it:
Initially, hospitals should be divided into solution shops, VAPs, and networks. Later, inexpensive business models should be given the chance to arise in all categories, such as mobile clinics taking the place of specialist hospitals.
After implementing these transformations, healthcare suppliers can revolutionize their business models such that patients can afford and acquire the healthcare they want.
Chapter 4 – Rendering tasks easier and less reliant on human abilities, technological enablers diminished expenses.
Prior to present-day technology, physicians could not comprehend what occurred beneath the skin of a patient. Rather, they carried out medical tests on the exterior and this is how they reached conclusions with regard to what happened inside.
However, physicians now utilize devices that take photos from the interior of bodies rather than conducting time-taking tests. The whole operation is less expensive, more efficacious, and easier. Evidently, developments in technology have greatly ameliorated healthcare.
The reason for this is the fact that technological enablers deal with issues on a micro-level and at the same time lower the expenses and decrease the dependency on human abilities. Then, what do technological enablers actually mean?
A technology that renders medical issues uncomplicated and reduces them to a routine is known as a technological enabler. It does not end here, though, as they also reduce expenses. Since people now can utilize devices such as diagnostic imaging technology, molecular diagnostics, and telecommunications, they no longer have to make substantial payments to accomplished experts.
Diagnostic imagining technology, for example, is a device snapping photos of the interior of patients and it is inexpensive, quick, and highly precise in results.

There are other ways through which technology reduces expenses, however. It changed the trust-on-instincts process to a straightforward rules-based one. To illustrate, inspecting an ill person’s symptoms, well-knowledgeable people, and a large accumulation of medical literature is an intricate and instinctual process. Fortunately, simple rules-based treatments are frequently able to prevent this inconvenience; they deal with the issues which have been accurately detected not according to the system but to the cause of the condition.
To give an example, as it is straight used in the cause of type 1 diabetes, insulin is counted as a wholly rules-based treatment.
The other way in which technology makes healthcare more affordable is through hiring affordable low-cost technicians rather than very accomplished and expensive ones. BMW is one example. For many years they have been developing the required algorithms to create super-realistic computer-based automobile models that entail virtual experiments. By substituting their very accomplished technicians with rules-based operation supervised by inexpensive technicians, the firm set aside a sizeable amount of money.
Chapter 5 – Healthcare is undergoing a change as technology provides precise and personalized medicines
You understand now that technology is vital for innovation to lessen the expenses. How does technology lessen expenses, though? Through creating a wholly distinct kind of medical service.
Precision and personalized medicine differ from the more conventional intuitive medicine. What is a technology enabler’s function in precision, though?
Intuitive medicine pays attention to symptoms; however, most illnesses came about with identical symptoms. Consider fever, for instance. If you had a fever, it could mean that you either have an ear infection or you are inflicted with Hodgkin’s Disease.
Later, conventional medicine diagnoses what is wrong after seeing symptoms and advise the necessary drugs to heal them. You might be advised to take some febrifuges to reduce fever but it will not eradicate the real cause.
Medical technology, however, is able to put a precise diagnose of illnesses and actually heal patients rather than lessening the effects of symptoms. To give an example, with the help of antibiotic treatment and of improvements in precision medicine employing microscopes and staining methods, scientists have found that human beings are comprised of microorganisms, some of which pose no danger while the others do.
Revealing this has helped physicians create precise antibiotics that eradicate harmful living creatures and stop them from breeding any illness.
Technology’s benefits to medicine do not end here, it makes it appropriate for personal use, too. Utilizing Information Technologies as a technological enabler supports extensive systems of interconnected firms with similar financial models to give information and react to the particular necessities of people.

Then, what does personalization mean?
Personalization concentrates on an individual’s particular state instead of the general health of other people whose diagnoses are the same as that of the individual. Applying the worldwide nature of social networking, IT can realize this by means of the Internet’s ‘’someone-like-me’’ sentiment. Partaking in a global society of people is an excellent route for patients to obtain information pertinent to their particular situations. Such particular knowledge has the utmost importance.
Chapter 6 – Innovating the business model of medical institutions will amount to a more efficacious and inexpensive.
Were you aware that the present-day medical institutions’ history goes back to Europe of the 1700s? They were constructed to deal with diseases such as tuberculosis and leprosy but actually became places where people awaited death. In the transition to the 19th century, they began to change themselves into esteemed scientific institutions of research.
Yet, however proficient these institutions were in curing tuberculosis at the beginning of the 1900s, or AIDS in the third quarter of the century, those who found solutions to issues formerly do not have to excel at problem-solving. Ultimately, present-day conditions are not the same as the conditions of the past.
But, as expensive medical institutions keep carrying out numerous a lot of research in the frame of mind of ‘‘do everything or everybody’’, they are struggling with rendering their health services cheaper and available. Actually, such a viewpoint obviously can never give a satisfying business model for healthcare. Below is the explanation:
This viewpoint merges two innately conflicting business models. The diagnosis and treatment of patients differ from each other in their own ways for profiting. In attempting to do them together, these institutions spend excessive amounts of money as they provide patients with too intricate and badly-provided services.
How will we overcome this issue?
Through the innovation of the business models of medical institutions, which means keeping a smaller number of them and splitting them into two separate models:

The solution shop is one of them and it concentrates on the diagnosis and frequently depends on costly technological innovations such as MRI devices. The other is VAP activities giving remedy to patients after their diagnosis is done.
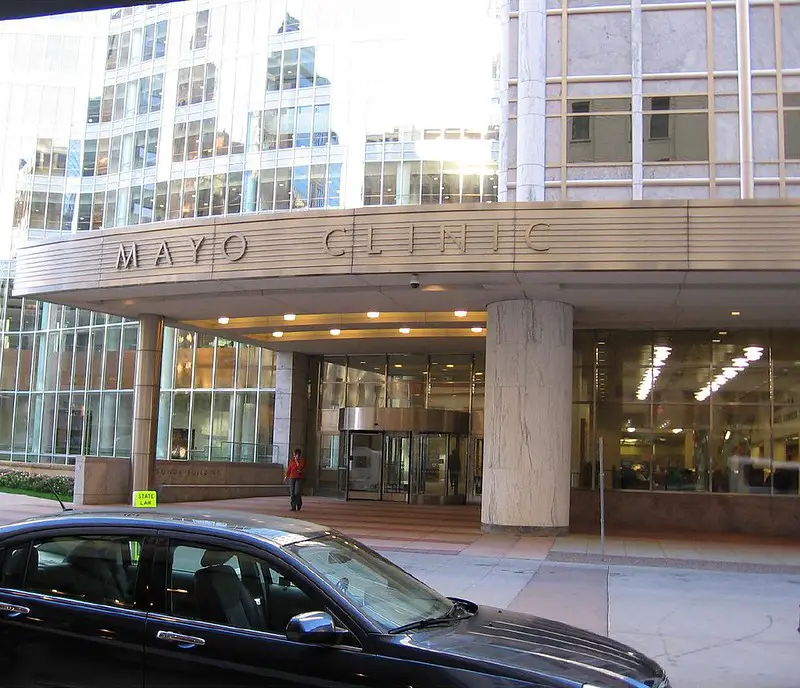
Thus, we have two options: build a complex hospital in which there is another hospital or construct two separate buildings. The Mayo Clinic, for example, is an instance of a solution shop giving very trustworthy diagnoses for more inexpensive expenses and directed patients with a diagnosis to another division of their medicinal facility to get VA processes on the basis of fee-for-outcome.
The Mayo Clinic’s separation into two different operations, each working on its model, allows each operation to work at a high standard while keeping expenses and losses at the lowest level.
Chapter 7 – The methods of doctors are not functioning anymore and have to undergo innovation by moving duties to other practitioners.
Medical institutions were not places that failed to merge two completely conflicting business models. Doctors are also liable for the same failure and, very similar to medical institutions, physicians must divide the conflicting business models they have.
Actually, the operations of doctors are functioning no more apparently. To give an example, doctors are normally engaged in four fields: putting diagnosis and curing diseases mostly linked to severe pain; superintending patients who suffer from prolonged illnesses; not only running examinations but also giving illness prevention, and detecting illnesses beforehand. Evidently, the duties of doctors are many – and the model comprises excessively numerous fields to guarantee both affordability and availability.
However, issues do not end here. The kind of physician who is able to concurrently handle many duties without failure is no more practical. The reason is that extremely a lot of potential diseases exist; our brain frankly is unable to follow them all.
To illustrate, back in 2007, doctors had the authority to give more than 13,000 medications in the US. How can one keep 13,000 medications in his head? Who can?

Hence, physicians have a myriad of responsibilities and it would be better if they distribute some of them to caretakers in hospitals and other doctors. To give an example, putting a diagnosis and curing diseases should be supervised by caretakers in walk-in clinics working on a VAP business model.
There are also other things but organizations utilizing a network-facilitator business model (gaining money from wellness, unlike doctors who gain money from sickness) should supervise patients with behavior-intensive illnesses.
When these transformations happen, doctors could obtain the freedom of keeping overseeing continuing wellness tests and at the same time utilize technology to rival solution shops operated by specialists. It may signify a provision of inexpensive on-site examinations and photographs, or perhaps online devices for diagnosis coalesce comprehensive research to provide main care doctors with more power for diagnosis, or telecommunications technologies enabling us to analyze data wherever they are.
Chapter 8 – Integrated capitation together with high-deductible insurance and health savings accounts can surmount issues through reimbursement.
You understand now that innovating the health-care system can make significant amelioration. However, if there is no reimbursement system that allows them, such transformations aren’t likely.
In fact, the present reimbursement system doesn’t function so properly usually. To give an example, the most prevalent sort of reimbursement, known as fee-for-service (FFS), signifies that, if you provide medical services, the amount of cash you spend is linear with the number of services you offer.
What makes it a wrong system?
Due to the fact that it sustains costly providers rather than making room for the rise of innovative ones. Because the costs of services are under the sway of important providers, those providers check to which new products and services money is invested, which is one explanation as to why medical institutions are more costly. The reason is that they give an excessive amount of services, which necessitate funding, whereby accelerating already increasing healthcare expenses.
A more suitable option would be a reimbursement system applying integrated capitation, in which all medical operations are accessible by only one contract that matches high-deductible insurance, or HDI, where your premiums are not as high whereas deductibles are greater, with health savings accounts, or HSAs.
In what way is it possible for integrated capitation to assist the health-care system in surmounting its present issues?
By supporting the advancement of innovative business models – a consequence it could cause by utilizing less costly therapeutic personnel such as nurse practitioners and doctor’s assistants. Saving money expended for these practitioners will provide an increase in profits for a practice.
But insurance is crucial for economic balance, as it guards our affluence against things such as extortionist hospital charges. It’s hence vital to put your money in HDI and HSAs to secure well-invested private health accounts.
To illustrate, not only do HSAs assist people to set aside money for therapeutical charges; they aid them in choosing options which tend to add up to their affluence since the money they keep in the bank accounts belong to them. This presents people with an economic motivation to lead a healthful life. When they follow this instruction, they will save really more money in the long-term.
Innovator’s Prescription by Clayton M. Christensen, Jerome H. Grossman, Jason Hwang Book Review
The health-care system does not operate properly and the cue of fixing it so that it functions properly is creatively innovating healthcare, which points to the split of general hospitals into separate business models providing separate services, and making money through their own methods. Technology can be helpful in the process by means of reducing the expenses of instinctual tests and specialized labor.
